Integrated dredging solutions
Drying of sludge and sediments
Why choose sludge dewatering with geotextiles?

- Efficient separation of solids and liquids in sludge
- Sludge volume reduction of up to 90%.
- Minimal environmental impact in the treatment of sludge and sediment
- Reduced operating and energy costs
- Ease of transport and disposal of dewatered sludge
- Possibility of recycling treated sludge for reuse in agriculture or construction


How does sludge dewatering using geotextiles work?
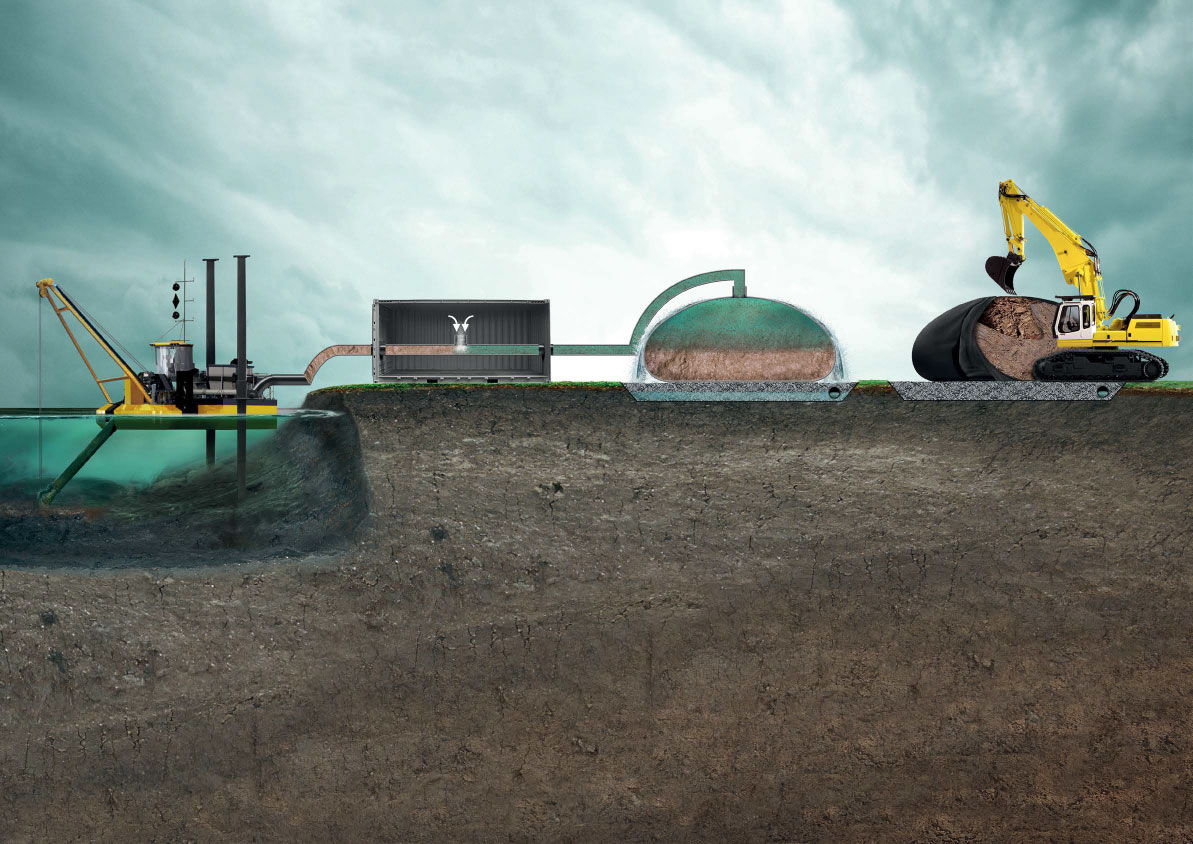

1. Removal of contaminated sediments
Advantages of geotextile
- Extremely high processing speed.
- Direct processing without the need for temporary storage.
- Online system without intermediate steps.
2. Packaging
The sludge is conditioned by a chemical flocculating agent, responsible for the agglomeration and clumping of fine particles suspended in the water into groups of larger particles, forming what are called “flocs”.
Advantages of geotextile
- Low mechanical loads acting on the flocs (lower rupture potential).
- Reduction (or elimination) of mechanical equipment required for the process.
3. Drying
Advantages of geotextile
- Possibility of water recirculation.
- Large storage capacity.
- Possibility of arranging the tubes at different levels.
- Simple capacity expansion (adding new modules)
4. Final withdrawal
Advantages of geotextile
- Encapsulating the sludge prevents its rehydration.
- Geotextile tubes also allow for permanent containment of sludge.
- It requires little space.
Applications of sludge dewatering using geotextiles
For these reasons, drying these materials before their final disposal appears to be the most economical solution.
Geotextile tubes offer a fast, cost-effective and viable dewatering solution for different types of materials.
Our sustainable sludge dewatering technology is ideal for:
- Removal of contaminated sediments in rivers and ports
- Restoration and recovery of beaches and marine ecosystems
- Waste and environmental management in infrastructure projects
- Treatment of sewage sludge and industrial effluents
- Recycling of dredged sediment for construction applications
- Sustainable management of contaminated dredging sludge

Sediments sometimes contain some degree of contamination with substances such as TBT, PCBs, and/or heavy metals like mercury and lead.

Mining processes continuously generate a significant volume of residues which, depending on their composition, can pose an environmental risk.

Industrial processes produce organic and mineral sludge that becomes easier to store, transport, or dispose of in the form of dried “cakes.”

Sludge from construction sites (excavations, drilling, etc.), with limited disposal space.

Sewage sludge (a by-product of biological processes in wastewater treatment plants). Smaller facilities generally lack mechanical sludge dewatering equipment.
Geotextile tubes for sludge dewatering


Made from geotextiles, high-tech fabrics specifically designed for this application, the tubes can be stacked on multiple levels to further enhance the system’s storage capacity. Significant cost savings can be achieved in terms of energy consumption, fuel, and maintenance costs associated with sludge transportation and dewatering, which are typical of other systems.
Geotextile tubes can also be used for the permanent containment of dried and consolidated materials without risk of rehydration (e.g. by rain), even during extended periods of operation.
As a result, a greater amount of dry solid residue is obtained compared to drying beds, for example. Geotextile tubes not only act as a durable and reliable containment system, but they also minimize to some extent the emission of the characteristic sludge odor.
Advantages of geotextile tubes
Three decisive factors
Decision criteria include the required dewatering capacity and operating speed, water quality, reuse (sludge or percolate), available space, and maintenance requirements. In addition to the above, and with equal importance, the capital investment associated with implementing the system must be considered. Overall, system efficiency is the most decisive factor in most projects. It is important that sludge removal from problem areas is carried out as quickly as possible, thus reducing the volume of sludge very quickly to facilitate its disposal, while also contributing to the reduction of overall project costs.
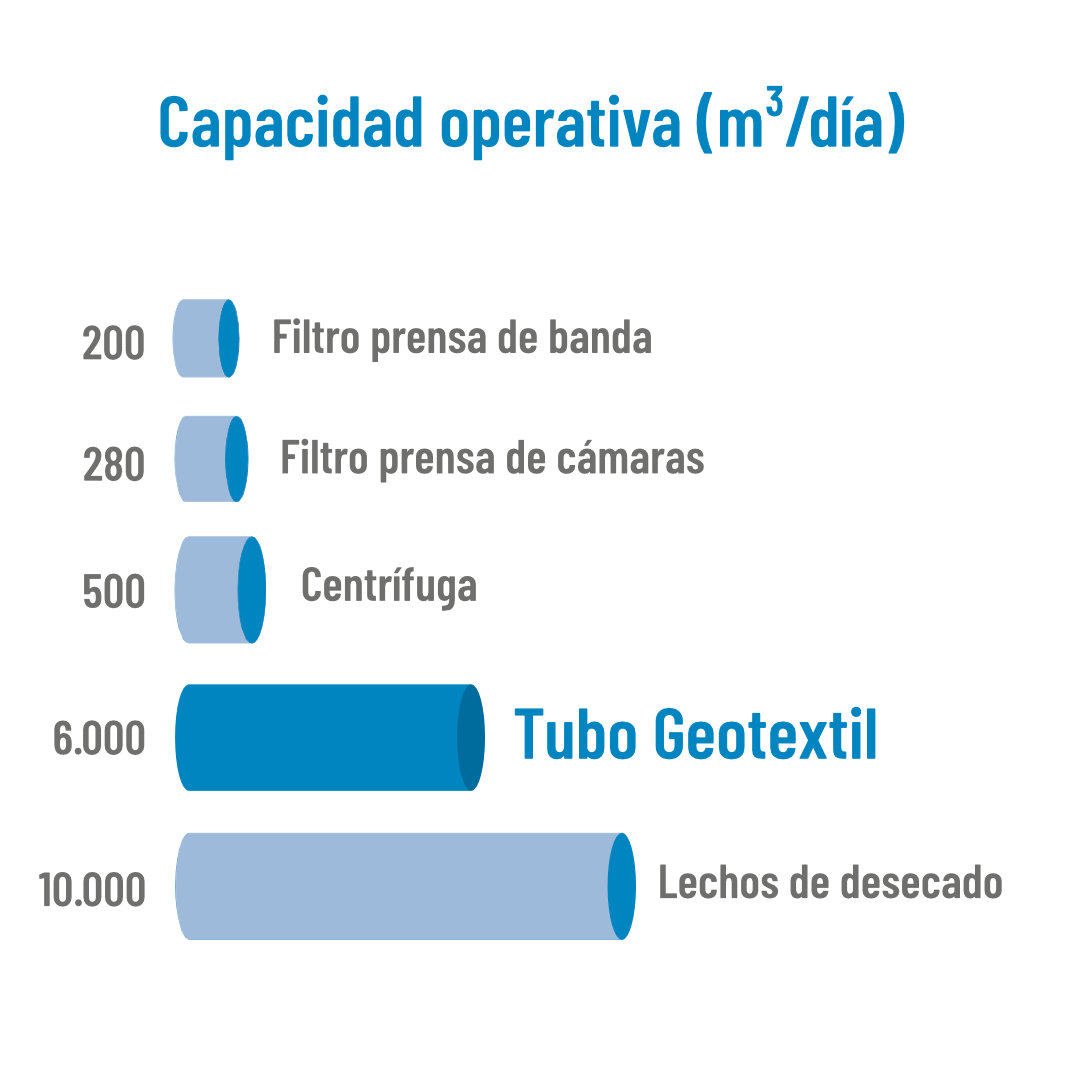
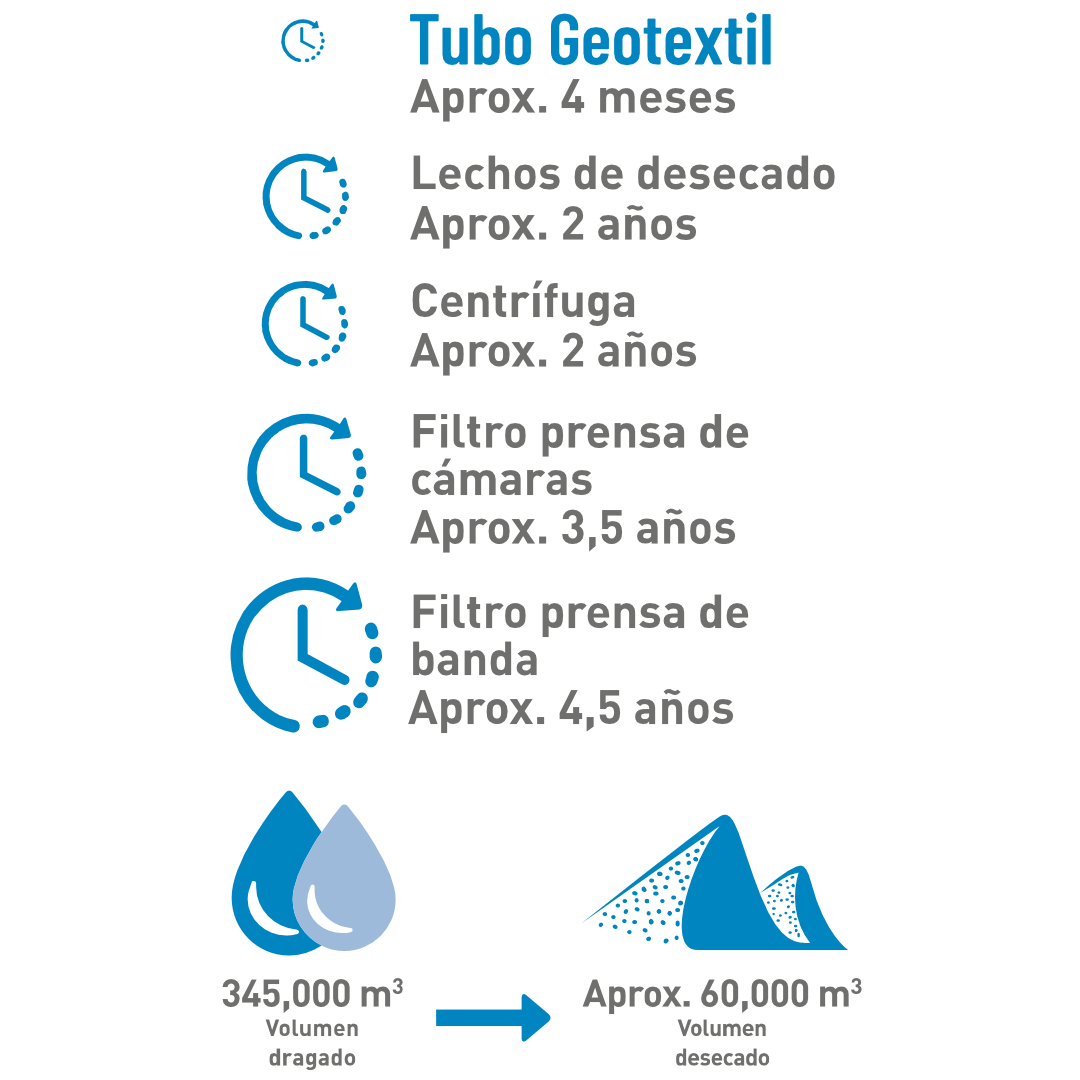
These three crucial factors are illustrated by the following project example for a sludge volume of 100,000 m3 and a dredged volume of 345,000 m3.


Operational capacity
Duration of the operation
In addition to the filling operation, the drying process also includes the subsequent volume reduction phase. With the development of the “cake” (dried sludge mass), the material becomes suitable for final disposal.
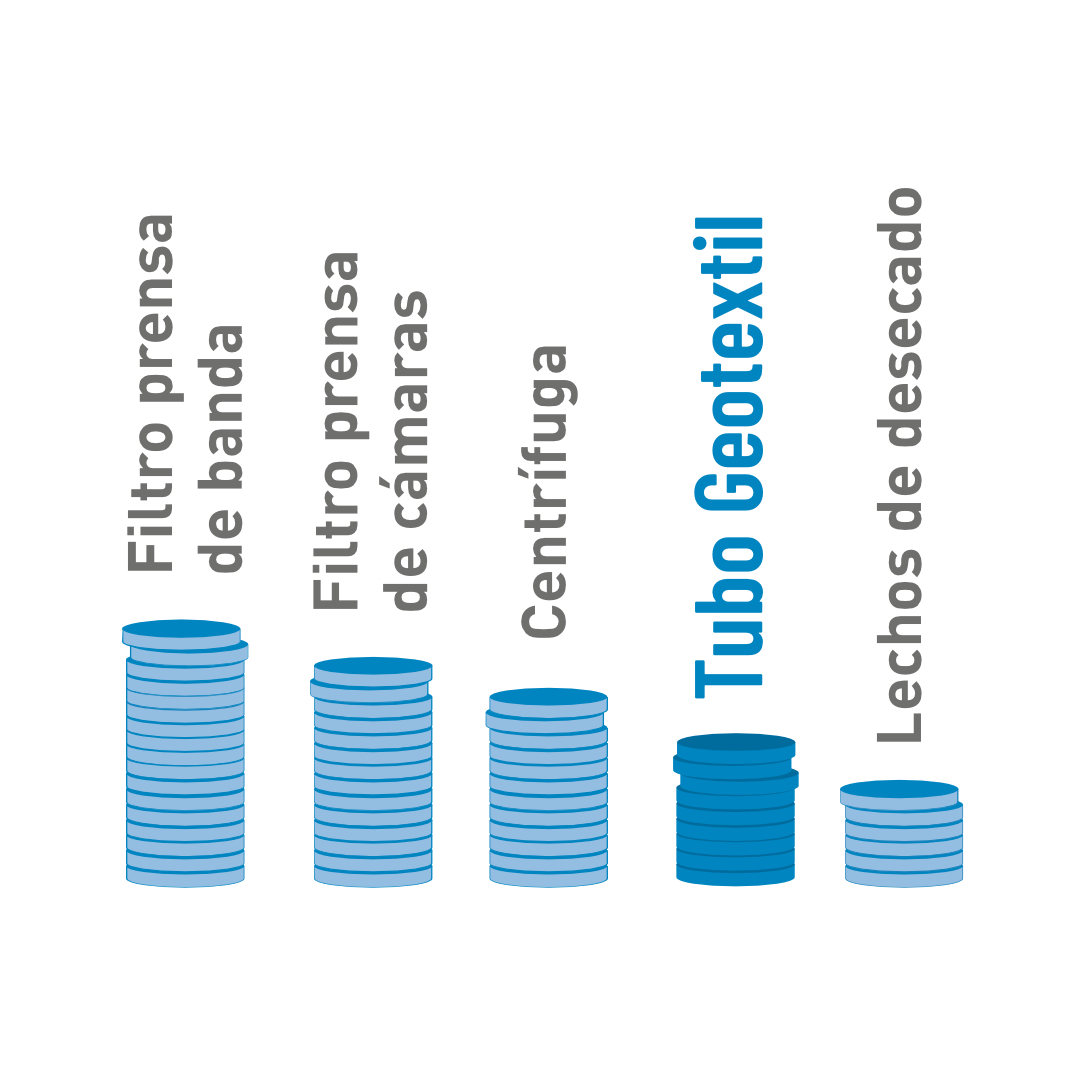
Geotextile bag modules allow this entire process to be carried out in a short period of time, comparable only to the use of mechanical means. Thus, the use of geotextile bags is equivalent to the operation of 12 centrifuges, 22 chamber filter presses or 30 belt filter presses.
The diagram shows the comparison based on the use of a single centrifuge or a filter press.
Project cost
Commitment to the environment
Contact us today!
If you are looking for effective and sustainable solutions for the maintenance and restoration of marine and coastal environments, don’t hesitate to contact us. Our team of experts is ready to help you protect and revitalise our precious coasts and oceans.